Programming Foundations#
Welcome to Programming Foundations! This book is part of the introductory programming course in the Bachelor’s program in Nanobiology at TU Delft. It aims to introduce students to programming in Python and working with computers. Many exercises and examples in this book are rooted in nanobiology, i.e., at the intersection of biology, physics, and mathematics.
How to use this book?
As you progress through the book, you will find that it consists of several elements:
Textual explanations
Code snippets which you can modify and execute directly in the book
Interactive quizzes for testing whether you understood the concepts
Worked-out examples showing how to approach problem solving with programming
Programming exercises at different difficulty levels, which are meant to be solved in your locally-installed coding environment
To use interactive elements of the book (code snippets and quizzes), you need to launch a “live version” of the book page which contains code and/or quizzes. You can do this by clicking the launch button at the top right side of the page, and then selecting “Live code”. If a page doesn’t have such a button (such as this introductory page), it means that it doesn’t contain any interactive elements. Typically, you will find a warning that a pages includes interactive elements on the top of such pages.
Programming has become an indispensable component in the skills repertoire of scientists and engineers. It is at the very core of theoretical research - modelling and simulations - as well as an invaluable supporting tool for experimental research - data analysis, visualization, and automation of repetitive tasks. Moreover, with the recent advances in artificial intelligence as well as the increasing number of large datasets produced by experiments, e.g., omics experiments, learning how to program will allow you to leverage these developments.
In this book, we will first familiarize ourselves with the core concepts and tools needed to work effectively with Python and computers in general. Next, we will explore the fundamentals of computer programming using Python, honing our skills with relevant examples from the field of nanobiology. As you progress through the book, you will notice that concepts build on one another. We will start with the basic building blocks of Python, such as variables. From there, we’ll learn how to gain more refined control over our code with flow control structures like conditional statements and loops. We will then move on to defining our own functions, working with data files, and creating plots in Python.
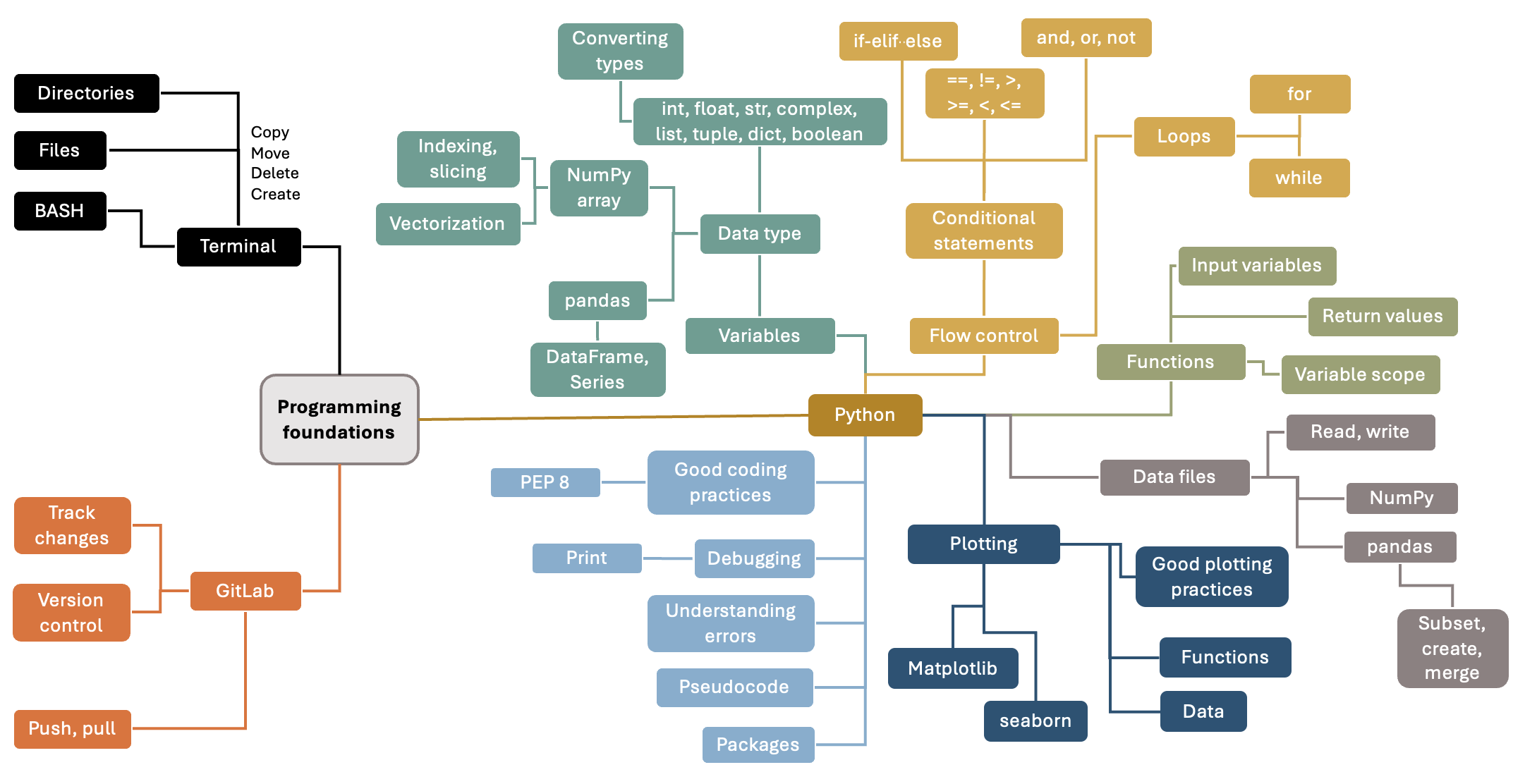
Fig. 1 Mind map of concepts covered by this book.#
Why do we focus on Python?
There are many available programming languages, so you may be asking yourself - why are we focusing on Python? Python is an open-source, intuitive, understandable as plain English, and beginner-friendly language. Since its first release in 1991, Python has been growing in popularity, and has become the most-used language among developers and data scientists today. In practice, this means that you will find a lot of documentation and troubleshooting support online, which will help you find solutions to programming tasks. In addition, Python proficiency is a valuable career skill today, both in and outside of academia.

Fig. 2 Python logo.#
While a first encounter with programming may be intimidating, we would like to invite you to keep the following in mind: programming is a learned skill, just like driving a car or playing a piano. That means that there is no inherent predisposition to be good at programming. In other words, everyone can master programming as long as they put sufficient time and effort into it. Because programming is a skill, the best way to learn it is by practicing. Therefore, do not hesitate to write code and make mistakes - that is the best way to learn.
Your journey into the world of programming starts here. We hope you will find it equal parts useful and fun!
Important
Help us improve this material! If you notice typos or mistakes in the book, or if you have any suggestions for book improvement, please let us know via this Google form.